Email: [email protected] Ligue agora! +55-11-3717-5537
Virtual Domains (VDOMs) are used to divide a FortiGate into two or more virtual units that function independently. VDOMs can provide separate security policies and, in NAT mode, completely separate configurations for routing and VPN services for each connected network.
There are two VDOM modes:
By default, most FortiGate units support 10 VDOMs, and many FortiGate models support purchasing a license key to increase the maximum number. Global settings are configured outside of a VDOM. They effect the entire FortiGate, and include settings such as interfaces, firmware, DNS, some logging and sandboxing options, and others. Global settings should only be changed by top level administrators.
In split-task VDOM mode, the FortiGate has two VDOMs: the management VDOM (root) and the traffic VDOM (FG-traffic).

The Management VDOM is used to manage the FortiGate, and cannot be used to process traffic.
The Traffic VDOM provides separate security policies, and is used to process all network traffic.
| The Management VDOM | The Traffic VDOM | |
|---|---|---|
| The following GUI sections are available: |
|
|
* Please note: Split-task VDOM mode is not available on all FortiGate models. The Fortinet Security Fabric supports split-task VDOM mode.
In multi VDOM mode, the FortiGate can have multiple VDOMs that function as independent units. One VDOM is used to manage global settings. The root VDOM cannot be deleted, and remains in the configuration even if it is not processing any traffic.
Multi VDOM mode isn’t available on all FortiGate models. The Fortinet Security Fabric does not support multi VDOM mode.
There are 3 types of Multi VDOM:
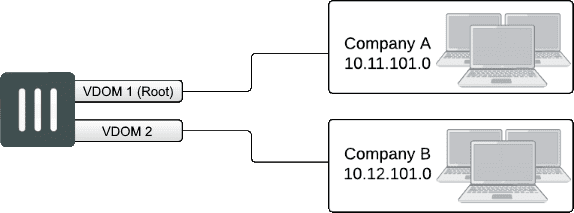
Multiple, completely separate VDOMs are created. Any VDOM can be the management VDOM, as long as it has Internet access. There are no inter-VDOM links, and each VDOM is independently managed.
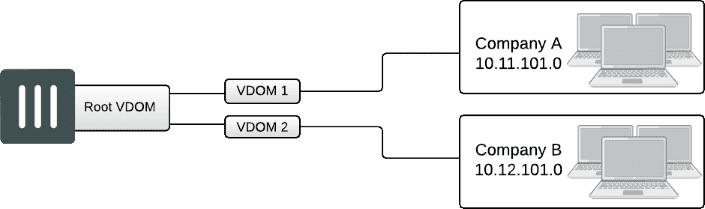
A management VDOM is located between the other VDOMs and the Internet, and the other VDOMs connect to the management VDOM with inter-VDOM links. The management VDOM has complete control over Internet access, including the types of traffic that are allowed in both directions. This can improve security, as there is only one point of ingress and egress. There is no communication between the other VDOMs.
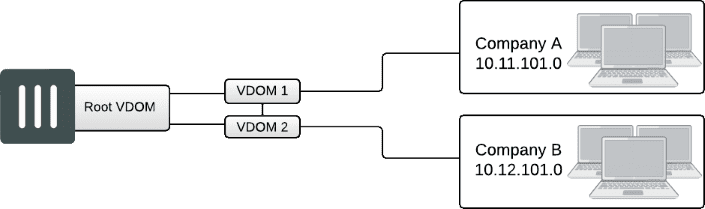
VDOMs can communicate with inter-VDOM links. In full-mesh configurations, all the VDOMs are interconnected. In partial-mesh configurations, only some of the VDOMs are interconnected.
| Current VDOM mode | New VDOM mode | Rule |
|---|---|---|
|
No VDOM |
Split-task VDOM |
Allowed |
|
Split-task VDOM |
No VDOM |
Allowed |
|
No VDOM |
Multi VDOM |
Allowed only if the FortiGate is not a member of a Security Fabric.Configuring the root FortiGate and downstream FortiGates |
|
Multi VDOM |
No VDOM |
Allowed |
|
Split-task VDOM |
Multi VDOM |
Allowed only if the FortiGate is not a member of a Security Fabric.Configuring the root FortiGate and downstream FortiGates |
|
Multi VDOM |
Split-task VDOM |
Not Allowed. User must first switch to No VDOM |
Note: All performance values are “up to” and vary depending on system configuration. IPsec VPN performance is based on 512 byte UDP packets using AES-256+SHA1.
1. IPS performance is measured using 1 Mbyte HTTP and Enterprise Traffic Mix.
2. SSL Inspection is measured with IPS enabled and HTTP traffic, using TLS v1.2 with AES256-SHA.
3. Application Control performance is measured with 64 Kbytes HTTP traffic.
4. NGFW performance is measured with IPS and Application Control enabled, based on Enterprise Traffic Mix.
5. Threat Protection performance is measured with IPS and Application Control and Malware protection enabled, based on Enterprise Traffic Mix.
6. CAPWAP performance is based on 1444 byte UDP packets.
* Maximum loading on each PoE/+ port is 30 W (802.3at).
| Licença | Upgrade license for adding VDOMs to FortiOS 5.4 and later | |
|---|---|
|
Upgrade license for adding 5 VDOMs to FortiOS 5.4 and later, limited by platform maximum VDOM capacity.
|
#FG-VDOM-5-UG |
|
Upgrade license for adding 15 VDOMs to FortiOS 5.4 and later, limited by platform maximum VDOM capacity.
|
#FG-VDOM-15-UG |
|
Upgrade license for adding 25 VDOMs to FortiOS 5.4 and later, limited by platform maximum VDOM capacity.
|
#FG-VDOM-25-UG |
|
Upgrade license for adding 50 VDOMs to FortiOS 5.4 and later, limited by platform maximum VDOM capacity.
|
#FG-VDOM-50-UG |
|
Upgrade license for adding 240 VDOMs to FortiOS 5.4 and later, limited by platform maximum VDOM capacity.
|
#FG-VDOM-240-UG |
| Licença | VDOM Subscription License for FortiGate S Series Subscription license for adding 5 VDOMs to FortiGate-VM S series running OS 7.0.1 or higher | |
| 1 ano – VDOM Subscription License for FortiGate S Series 1 Year Subscription license for adding VDOMs to FortiGate-VM S series running OS 6.4.9/7.0.2 or higher. This is a seat SKU where the total number of vdoms must be added as seats in an increment of 5 and the minimal order is 5 vdoms | #FC1-10-FGVVS-498-02-12 |
| 3 anos – VDOM Subscription License for FortiGate S Series 3 Year Subscription license for adding VDOMs to FortiGate-VM S series running OS 6.4.9/7.0.2 or higher. This is a seat SKU where the total number of vdoms must be added as seats in an increment of 5 and the minimal order is 5 vdoms | #FC1-10-FGVVS-498-02-36 |
| 5 anos – VDOM Subscription License for FortiGate S Series 5 Year Subscription license for adding VDOMs to FortiGate-VM S series running OS 6.4.9/7.0.2 or higher. This is a seat SKU where the total number of vdoms must be added as seats in an increment of 5 and the minimal order is 5 vdoms | #FC1-10-FGVVS-498-02-60 |
| Licença | ADOM Subscription License for FortiAnalyzer S-Series ADOM subscription license for adding 1 ADOM to FortiAnalyzer-VM S models running OS 6.4 or higher | |
| 1 ano – 1 Year ADOM Subscription License for adding 1 ADOM to FortiAnalyzer-VM S models running OS 6.4 or higher | #FC-10-AZVMS-230-01-12 |
| 2 anos – 2 Years ADOM Subscription License for adding 1 ADOM to FortiAnalyzer-VM S models running OS 6.4 or higher | #FC-10-AZVMS-230-01-24 |
| 3 anos – 3 Years ADOM Subscription License for adding 1 ADOM to FortiAnalyzer-VM S models running OS 6.4 or higher | #FC-10-AZVMS-230-01-36 |
| 4 anos – 4 Years ADOM Subscription License for adding 1 ADOM to FortiAnalyzer-VM S models running OS 6.4 or higher | #FC-10-AZVMS-230-01-60 |
| Licença | ADOM Subscription License for FortiManager S-Series ADOM Subscription license for adding 1 ADOM to FortiManager-VM S models running OS 6.4 or higher | |
| 1 ano – FortiManager 1 Year ADOM Subscription License for adding 1 ADOM to FortiManager-VM S models running OS 6.4 or higher | #FC-10-FMGVS-230-01-12 |
| 2 anos – FortiManager 2 Years ADOM Subscription License for adding 1 ADOM to FortiManager-VM S models running OS 6.4 or higher | #FC-10-FMGVS-230-01-24 |
| 3 anos – FortiManager 3 Year ADOM Subscription License for adding 1 ADOM to FortiManager-VM S models running OS 6.4 or higher | #FC-10-FMGVS-230-01-36 |
| 5 anos – FortiManager 5 Year ADOM Subscription License for adding 1 ADOM to FortiManager-VM S models running OS 6.4 or higher | #FC-10-FMGVS-230-01-60 |
| Licença | Upgrade license for adding 1 ADOM to FortiAnalyzer hardware G models 1000 Series and above. | |
| 1 ano – Upgrade license for adding 1 ADOM to FortiAnalyzer hardware G models 1000 Series and above | #FAZ-ADOM-1-UG |